
FET TRANSISTOR AS A SWITCH FULL
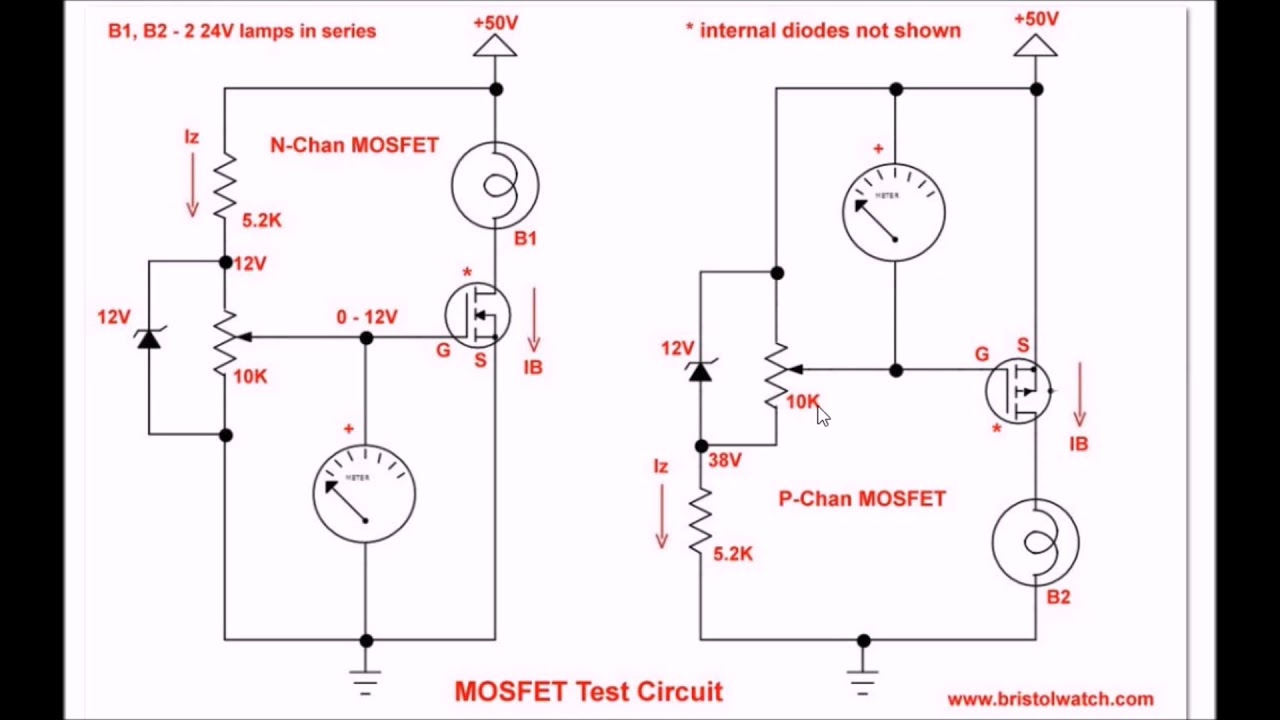
While a MOSFET might turn on at a relatively low voltage, it is only capable of carrying full current at a specified gate-source voltage.

This is similar to the base-emitter voltage of a regular BJT, but with MOSFETs, this voltage is not as sharply defined. This depends on the application – power MOSFETs are available with breakdown ratings as low as 20V and as high as 1200V, and currents ranging from milliamps to kiloamps, a full six decades. There are a few important points considerations when using a MOSFET as a switch.ĭrain-to-source breakdown voltage and drain current: However, like the BJT, this property is not linear, that is, the resistance does not decrease linearly with applied gate voltage, as shown in the below figure from the datasheet of the popular IRF3205, while we are talking about internal resistance heat plays a key role when it comes to internal resistance.įor the most part, this does not matter, since power MOSFETs are intended to be used for switching applications, though linear use is possible. The MOSFET can be thought of as a voltage-controlled variable resistor, just like the BJT transistor can be considered a current-controlled current source. Most power MOSFET schematic symbols are drawn showing the parasitic diode. Technically speaking, a FET is inherently bidirectional, but the way power MOSFETs are constructed on the silicon-level adds a parasitic anti-parallel diode across the drain and source, which makes the MOSFET conduct when the voltage across it is reversed, which is something to keep in mind. Like Bipolar Junction Transistor or BJT, MOSFET is a three-terminal device, the three terminals being the GATE, the drain, and the SOURCE, with the gate controlling the conduction between the drain and source terminals. In one of our previous articles, we have discussed What is MOSFET: Its Construction, Types, and Working you can check that out if you want t to learn about the basics of a MOSFET. So, in this article, we will talk about different ways to switch on and off a MOSFET and in the end, we will look at some practical examples that show how this affects the MOSFET. MOSFETs are preferred for their low conduction losses, low switching losses, and as the gate of the MOSFET is made out of capacitors it has a zero DC gate current. Almost all modern-day switching supplies use some form of power MOSFETs as their switching elements. Ever since the advent of the power MOSFET in the 1980s, power switching has become faster and more efficient. Depending on this gate voltage we can change the conductivity and thus we can use it as a switch or as an amplifier like we use a Transistor as a switch or as an amplifier.
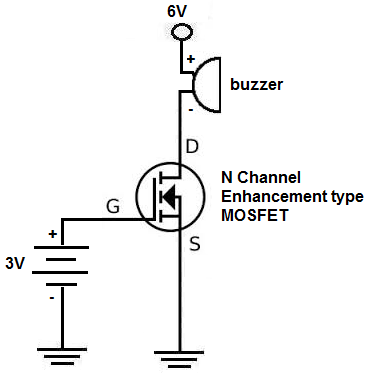
Similarly, the gate voltage determines the conductivity of the device. For simplicity, you can imagine this gate as like a water tap you rotate the tap counter-clockwise the water starts flowing out of the tap, you rotate it clockwise water stops flowing from the tap. MOSFET stands for Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor, which has a gate. For higher voltages the gate-source voltage would have to be clamped with a zener diode.MOSFET is a transistor that uses field effect. The NMOS can be the type that turns on full at about 5 VDC or 10 VDC, depending on the logic driving it.ĮDIT: Because the PMOS is grounded when it is turned on, the limit for Vin is 20 VDC or less. I should note that the NMOS transistor will be exposed to the same Vin voltage through the bias resistor, which is used to make sure the PMOS is OFF if 'EN' is low or at its ground/source voltage (zero volts). The maximum voltage limit for MOSFETs right now is about 700 VDC. It could be the main power switch for all sorts of gadgets while keeping 'EN' isolated. It can switch an extremely high voltage on or off, such as 300 VDC for a long string of LEDs. The PMOS transistor could also be most any PNP transistor. Also the source may not tolerate high voltage above 3.3 VDC or 5 VDC logic voltage at its output terminals. The purpose of this very common design, which includes BJT transistors as well, is to isolate the 'EN' signal, which can be from a low voltage source.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
